Background of Yanluowang
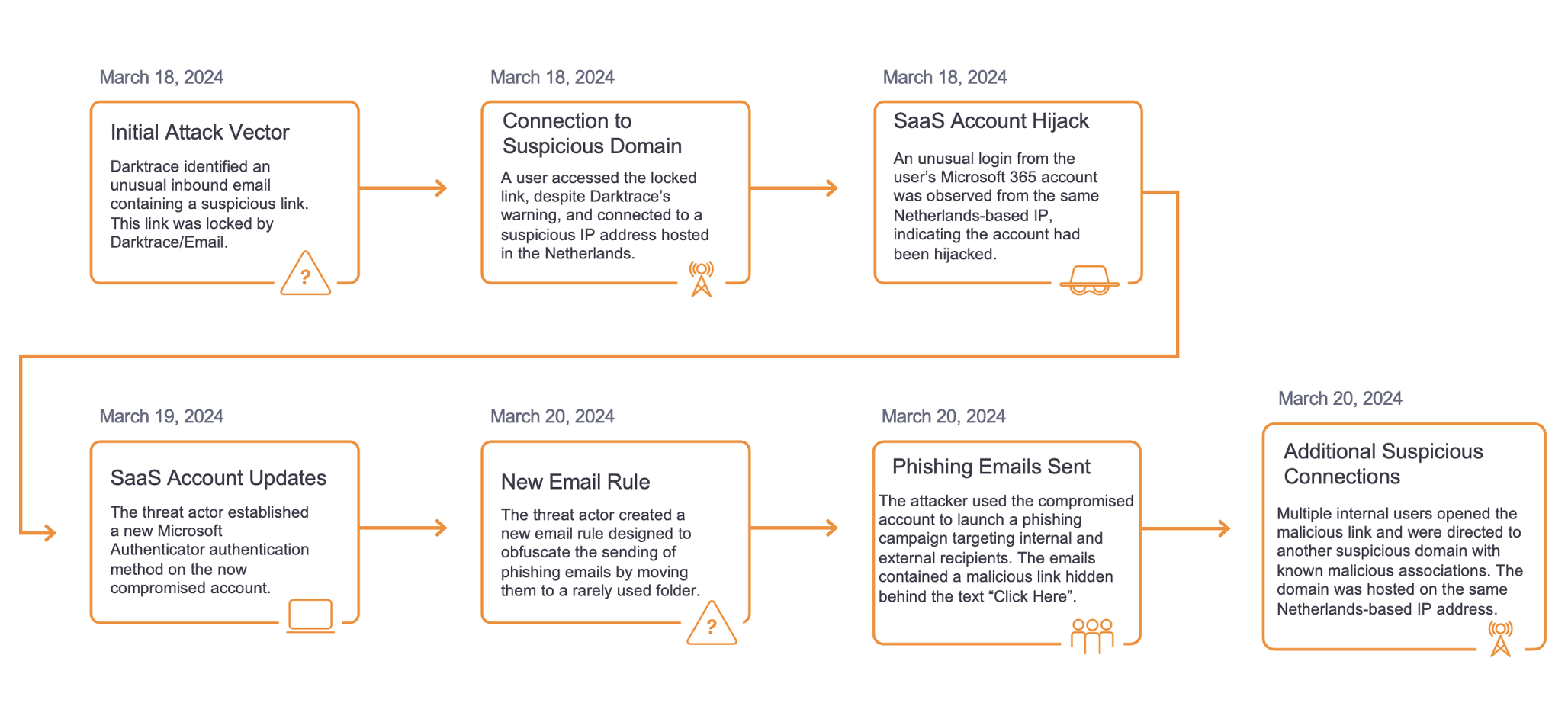
Yanluowang ransomware, also known as Dryxiphia, was first spotted in October 2021 by Symantec’s Threat Hunter Team. However, it has been operational since August 2021, when a threat actor used it to attack U.S. corporations. Said attack shared similar TTPs with ransomware Thieflock, designed by Fivehands ransomware gangs. This connection alluded to a possible link between the two through the presence or influence of an affiliate. The group has been known for successfully ransoming organisations globally, particularly those in the financial, manufacturing, IT services, consultancy, and engineering sectors.
Yanluowang attacks typically begin with initial reconnaissance, followed by credential harvesting and data exfiltration before finally encrypting the victim’s files. Once deployed on compromised networks, Yanluowang halts hypervisor virtual machines, all running processes and encrypts files using the “.yanluowang” extension. A file with name README.txt, containing a ransom note is also dropped. The note also warns victims against contacting law enforcement, recovery companies or attempting to decrypt the files themselves. Failure to follow this advice would result in distributed denial of service attacks against a victim, its employees and business partners. Followed by another attack, a few weeks later, in which all the victim’s files would be deleted.
The group’s name “Yanluowang” was inspired by the Chinese mythological figure Yanluowang, suggesting the group’s possible Chinese origin. However, the recent leak of chat logs belonging to the group, revealed those involved in the organisation spoke Russian.
Leak of Yanluowang’s chat logs
On the 31st of October, a Twitter user named @yanluowangleaks shared the matrix chat and server leaks of the Yanluowang ransomware gang, alongside the builder and decryption source. In total, six files contained internal conversations between the group’s members. From the analysis of these chats, at least eighteen people have been involved in Yanluowang operations.

Potential members: ‘@killanas', '@saint', '@stealer', '@djonny', '@calls', '@felix', '@win32', '@nets', '@seeyousoon', '@shoker', '@ddos', '@gykko', '@loader1', '@guki', '@shiwa', '@zztop', '@al', '@coder1'
Most active members: ‘@saint’, ‘@killanas’, ‘@guki’, ‘@felix’, ‘@stealer’.
To make the most sense out of the data that we analyzed, we combined the findings into two categories: tactics and organization.
Tactics
From the leaked chat logs, several insights into the group’s operational security and TTPs were gained. Firstly, members were not aware of each other’s offline identities. Secondly, discussions surrounding security precautions for moving finances were discussed by members @killanas and @felix. The two exchanged recommendations on reliable currency exchange platforms as well as which ones to avoid that were known to leak data to law enforcement. The members also expressed paranoia over being caught with substantial amounts of money and therefore took precautions such as withdrawing smaller amounts of cash or using QR codes for withdrawals.
Additionally, the chat logs exposed the TTPs of Yanluowang. Exchanges between the group’s members @stealer, @calls and @saint, explored the possibilities of conducting attacks against critical infrastructure. One of these members, @call, was also quick to emphasise that Yanluowang would not target the critical infrastructure of former Soviet countries. Beyond targets, the chat logs also highlighted Yanluowang’s use of the ransomware, PayloadBIN but also that attacks that involved it may potentially have been misattributed to another ransomware actor, Evil Corp.
Further insight surrounding Yanluowang’s source code was also gained as it was revealed that it had been previously published on XSS.is as a downloadable file. The conversations surrounding this revealed that two members, @killanas and @saint, suspected @stealer was responsible for the leak. This suspicion was supported by @saint, defending another member whom he had known for eight years. It was later revealed that the code had been shared after a request to purchase it was made by a Chinese national. @saint also used their personal connections to have the download link removed from XSS.is. These connections indicate that some members of Yanluowang are well embedded in the ransomware and wider cybercrime community.
Another insight gained from the leaked chat logs was an expression by @saint in support of Ukraine, stating, “We stand with Ukraine” on the negotiation page of Yanluowang’s website. This action reflects a similar trend observed among threat actors where they have taken sides in the Russia-Ukraine conflict.
Regarding Yanluowang’s engagement with other groups, it was found that a former member of Conti had joined the group. This inference was made by @saint when a conversation regarding the Conti leak revolved around the possible identification of the now Yanluowang member @guki, in the Conti files. It was also commented that Conti was losing a considerable number of its members who were then looking for new work. Conversations about other ransomware groups were had with the mentioning of the REVIL group by @saint, specifically stating that five arrested members of the gang were former classmates. He backed his statement by attaching the article about it, to which @djonny replies that those are indeed REVIL members and that he knows it from his sources.
Organization
When going through the chat logs, several observations were made that can offer some insights into the group's organizational structure. In one of the leaked files, user @saint was the one to publish the requirements for the group's ".onion" website and was also observed instructing other users on the tasks they had to complete. Based on this, @saint could be considered the leader of the group. Additionally, there was evidence indicating that a few users could be in their 30s or 40s, while most participants are in their 20s.
More details regarding Yanluowang's organizational structure were discussed deeper into the leak. The examples indicate various sub-groups within the Yanlouwang group and that a specific person coordinates each group. From the logs, there is a high probability that @killanas is the leader of the development team and has several people working under him. It is also possible that @stealer is on the same level as @killanas and is potentially the supervisor of another team within the group. This was corroborated when @stealer expressed concerns about the absence of certain group members on several occasions. There is also evidence showing that he was one of three people with access to the source code of the group.
Role delineation within the group was also quite clear, with each user having specific tasks: DDoS (distributed denial of service) attacks, social engineering, victim negotiations, pentesting or development, to mention a few. When it came to recruiting new members, mostly pentesters, Yanluowang would recruit through XSS.is and Exploit.in forums.
Underground analysis and members’ identification
From the leaked chat logs, several “.onion” URLs were extracted; however, upon further investigation, each site had been taken offline and removed from the TOR hashring. This suggests that Yanluowang may have halted all operations. One of the users on XSS.is posted a picture showing that the Yanluowang onion website was hacked, stating, “CHECKMATE!! YANLUOWANG CHATS HACKED @YANLUOWANGLEAKS TIME’S UP!!”.

After learning that Yanluowang used Russian Web Forums, we did an additional search to see what we could find about the group and the mentioned nicknames.
By searching through XSS.Is we managed to identify the user registered as @yanluowang. The date of the registration on the forum dates to 15 March 2022. Curiously, at the time of analysis, we noticed the user was online. There were in total 20 messages posted by @yanluowang, with a few publications indicating the group is looking for new pentesters.


While going through the messages, it was noticed the reaction posted by another user identified as @Sa1ntJohn, which could be the gang member @saint.

Looking further, we identified that user @Ekranoplan published three links to the website doxbin.com containing information about three potential members of the YanLuoWang gang: @killanas/coder, @hardbass and @Joe/Uncle. The profile information was published by the user @Xander2727.



If the provided information is correct, two group members are Russian and in their 30s, while another member is Ukrainian and in his 20s. One of the members, @killanas, who was also referenced in chat logs, is identified as the lead developer of the Yanluowang group; giving the interpretation of the chat leaks a high-level of confidence. Another two members, who were not referenced in the logs, took roles as Cracked Software/Malware provider and English translator/Victim Negotiator.
Implications for the wider ransomware landscape
To conclude with the potential implications of this leak, we have corroborated the evidence gathered throughout this investigation and employed contrarian analytical techniques. The ascertained implications that follow our mainline judgement, supporting evidence and our current analytical view on the matter can be categorized into three key components of this leak:
Impact on the ransomware landscape
The leak of Yanluowang’s chat logs has several implications for the broader ransomware landscape. This leak, much like the Conti leak in March, spells the end for Yanluowang operations for the time being, given how much of the group’s inner workings it has exposed. This could have an adverse effect. While Yanluowang did not control as large of a share of the ransomware market as Conti did, their downfall will undoubtedly create a vacuum space for established groups for their market share. The latter being a consequence of the release of their source code and build tools.
Source code
The release of Yanluowang’s source code has several outcomes. If the recipients have no malintent, it could aid in reverse engineering the ransomware, like how a decryption tool for Yanluowng was released earlier this year. An alternative scenario is that the publication of the source code will increase the reach and deployment of this ransomware in the future, in adapted or modified versions by other threat actors. Reusing leaked material is notorious among ransomware actors, as seen in the past, when Babuk’s source code was leaked and led to the development of several variants based on this leak, including Rook and Pandora. This could also make it harder to attribute attacks to one specific group.
Members
The migration of unexposed Yanluowang members to other ransomware gangs could further add to the proliferation of ransomware groups. Such forms of spreading ransomware have been documented in the past when former Conti members repurposed their tactics to join efforts with an initial access broker, UAC-0098. Yet, the absence of evidence from members expressing and/or acting upon this claim requires further investigation and analysis. However, as there is no evidence of absence – this implication is based on the previously observed behavior from members of other ransomware gangs.