Griefランサムウェア、これはPayOrGriefとも呼ばれていましたが、2021年の中ごろから末にかけてその被害が急速に知られるようになりました。このマルウェアの背後のギャングは四重恐喝ランサムウェア 戦術を使用し、地方自治体や学校区を含む幅広い組織を標的にしました。
2021年7月、このランサムウェアがサイバーセキュリティ業界に最初に知られてからわずか数週間後、Griefはギリシャで2番目に大きい都市、テッサロニキを標的としました。2000万ドルの身代金要求に対し、市のセキュリティチームはそのすべてのウェブサイトと公的サービスのシャットダウンを余儀なくされ、この侵害に対する全面的調査を開始しました。
2人組:GriefとDoppelPaymer
From its emergence in May 2021, Grief used novel malware which confounded security tools trained on historical attacks. By July, however, the sophistication and efficiency of the group’s attacks led many to suspect that Grief’s operators had experience beyond their supposed two months of operation.
Grief is now widely reported to be a rebrand of the DoppelPaymer ransomware gang, which ended its operations in May 2021 and was believed to be affiliated with the Russian ransomware gang Evil Corp. After adopting the new moniker, however, Grief regularly blew past traditional security tools, amassing well over $10 million in ransom payments in just four months.
Adaptations and rebrands are common techniques adopted by criminal gangs using the Ransomware-as-a-Service business model. The success of Grief’s rebrand illustrates how rapidly a ransomware group can update its attacks and render them unrecognizable to signature-based tools.
Revealing Grief’s tricks with Cyber AI Analyst
In July 2021, PayOrGrief targeted a European manufacturing company which had Darktrace deployed across its network. Darktrace’s early detection of the attack, along with the real-time visibility into its lifecycle offered by Darktrace’s Cyber AI Analyst, meant that each stage of the attack was clear to see.

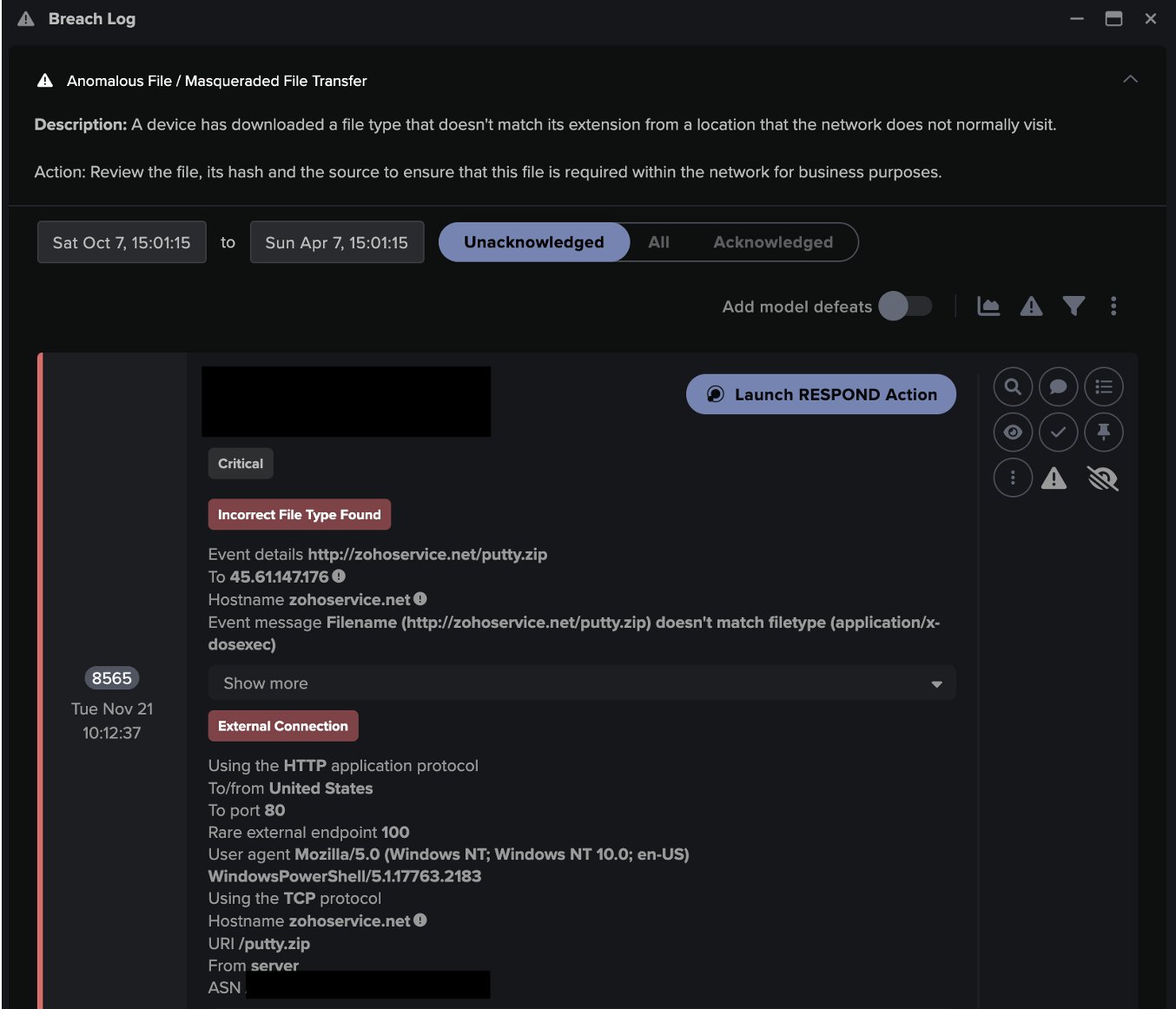
The initial intrusion compromised four devices, which Darktrace detected when these devices connected to rare external IPs and downloaded encoded text files. It is likely that the devices were compromised as the result of a targeted phishing campaign, which are often used in Grief attacks as a way of injecting malware such as Dridex onto devices. If deployed within the targeted organization, Antigena Email would have identified the phishing campaign and halted it, before it reached employee inboxes. In this case, however, the attack continued.
Following the initial compromise, C2 (Command and Control) connections were made over an encrypted channel using invalid SSL certificates. An upload of 50MB of data was made from one of the infected devices to the company’s corporate server, which gave the attackers access to the company’s crown jewels: its most sensitive data. From this privileged position, and with keep-alive beacons in place, the attack was ready for detonation.
Several devices were detected attempting to upload data totaling more than 100 GB to the external file storage platform, Mega, using encrypted HTTPS on port 443. However, the attackers did not receive the total package of data they had expected. The organization had deployed Darktrace’s Autonomous Response to protect its key assets and most sensitive data. The AI recognized the anomalous behavior as a significant deviation from the business’s normal ‘pattern of life’ and autonomously blocked uploads from protected devices, preventing exfiltration wherever it was able to do so.

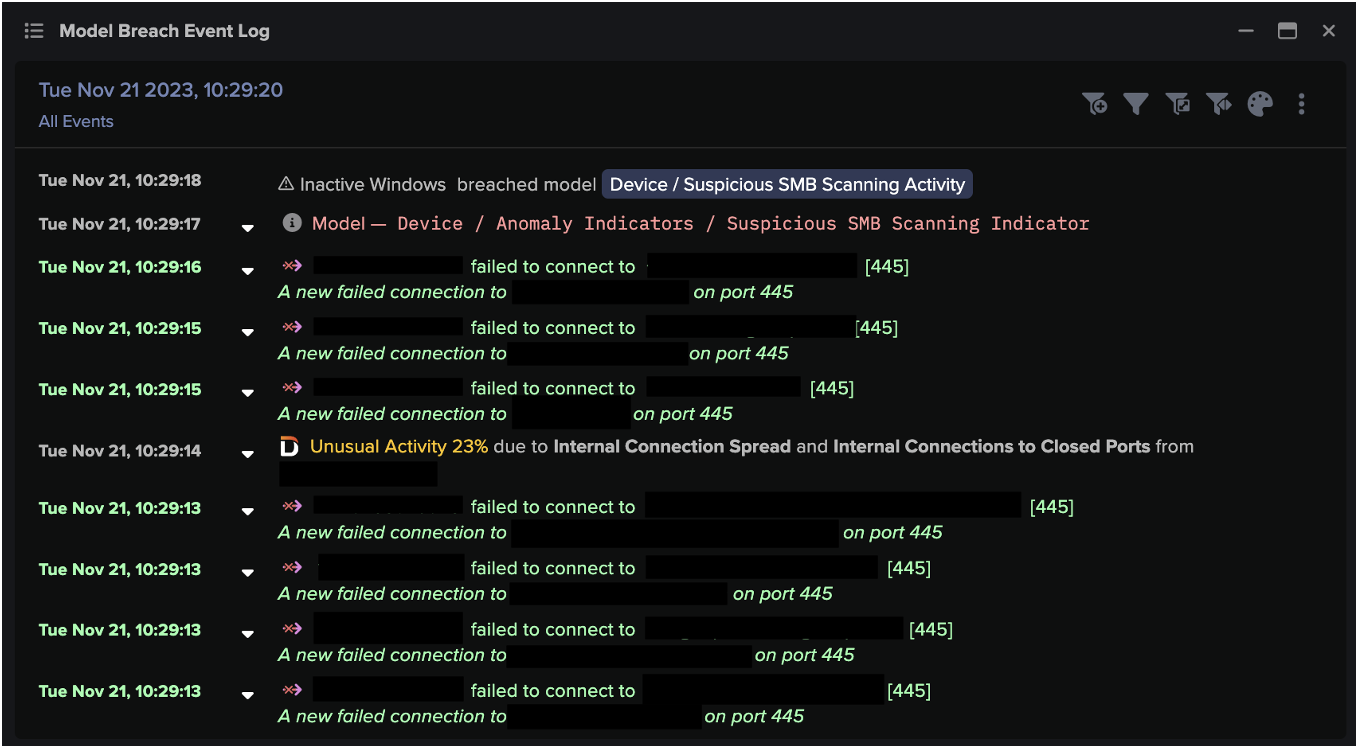
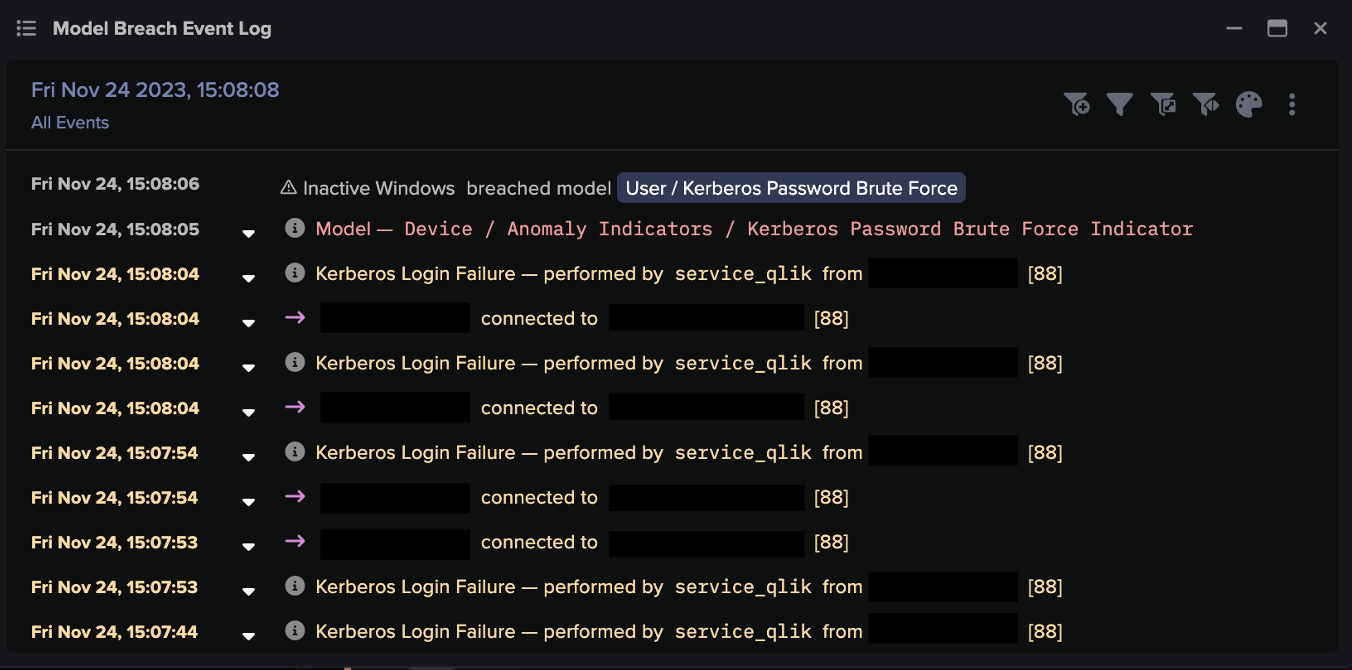
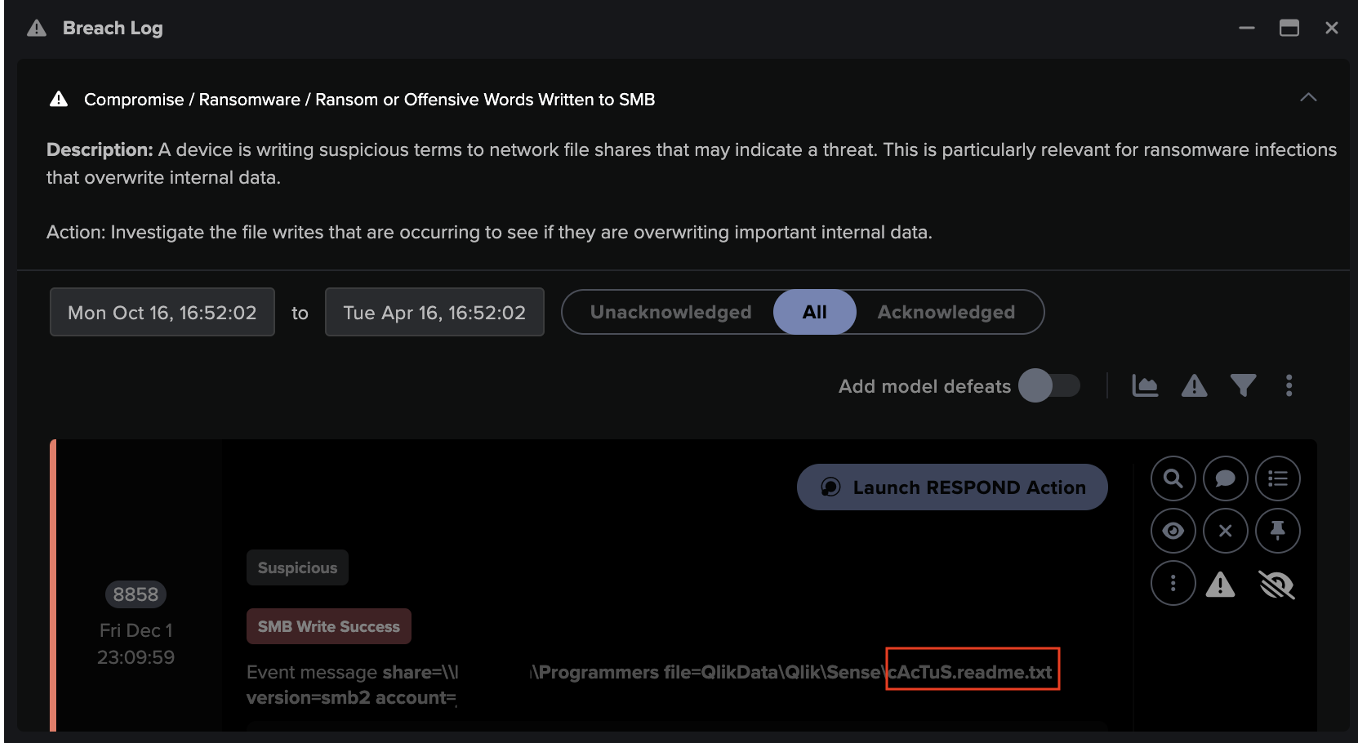
The attackers then continued to spread through the digital environment. Using ‘Living off the Land’ techniques including RDP and SMB, they performed internal reconnaissance, escalated their privileges and moved laterally to additional digital assets. With access to new admin credentials, just ten hours after the initial C2 communications, the attackers commenced ransomware encryption.
It’s highly possible, therefore, that Grief has targeted Darktrace customers previously and been neutralized too early for the attack to be identified and attributed. In this instance, the organization had deployed Autonomous Response only on certain areas of the network, and we are therefore able to see how the attack progressed on unprotected devices.
Unusual suspects
The Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) for Grief ransomware have now been incorporated by many traditional security tools, but this is a short-term solution, and won’t account for further changes in both threat actor tactics and the digital environments they target. Once the Grief moniker has been exhausted, it is more than likely that another will be adopted in its place.
The AI-driven approach to cyber security tackles threats regardless of when and where they arrive, or what name they arrive under. By focusing on developing its sophisticated understanding of the entire digital estate, Darktrace’s Autonomous Response targets specific anomalies with specific, proportionate responses, even when they are part of entirely novel attacks. And when given the freedom to take action against these threats the moment they’re detected, Autonomous Response can ensure that organizations stay protected even when human teams are unavailable.
Thanks to Darktrace analyst Beverly McCann for her insights on the above threat find.
Technical details
Darktrace model detections
- Device / Suspicious SMB Scanning Activity
- Device / New User Agents
- Anomalous Server Activity / Rare External from Server
- Compliance / External Windows Communications
- Anomalous Connection / Application Protocol on Uncommon Port
- Anomalous Connection / Anomalous SSL without SNI to New External
- Anomalous Connection / Rare External SSL Self-Signed
- Anomalous Connection / Multiple Connections to New External TCP Port
- Anomalous Connection / New User Agent to IP Without Hostname
- Compliance / Remote Management Tool on Server
- Anomalous Server Activity / Outgoing from Server
- Anomalous Connection / Multiple HTTP POSTs to Rare Hostname
- Anomalous Connection / Data Sent to Rare Domain
- Anomalous Connection / Lots of New Connections
- Unusual Activity / Unusual File Storage Data Transfer
- Unusual Activity / Enhanced Unusual External Data Transfer [Enhanced Monitoring]
- Anomalous Connection / Uncommon 1GiB Outbound
- Unusual Activity / Unusual External Data to New Ips
- Anomalous Connection / SMB Enumeration
- Multiple Device Correlations / Behavioral Change Across Multiple Devices
- Device / New or Uncommon WMI Activity
- Unusual Activity / Unusual External Connections
- Device / ICMP Address Scan
- Anomalous Connection / Unusual Admin RDP Session
- Compliance / SMB Version 1 Usage
- Anomalous Connection / Unusual SMB Version 1
- Anomalous File / Internal / Additional Extension Appended to SMB File
- Unusual Activity / Anomalous SMB Move and Write
- Compromise / Ransomware / Suspicious SMB Activity [Enhanced Monitoring]
- Anomalous Connection / Suspicious Read Write Ratio and Unusual SMB
- Anomalous Connection / New or Uncommon Service Control
- Device / New or Unusual Remote Command Execution
- User / New Admin Credentials On Client
- Device / New or Uncommon SMB Named Pipe
- Device / Multiple Lateral Movement Model Breaches [Enhanced Monitoring]
- Anomalous Connection / Suspicious Read Write Ratio
- Device / SMA Lateral Movement
- Anomalous File / Internal / Unusual Internal EXE File Transfer
- Anomalous Server Activity / Unusual Unresponsive Server
- Device / Internet Facing Device with High Priority Alert
- Multiple Device Correlations / Spreading Unusual SMB Activity
- Multiple Device Correlations / Multiple Devices Breaching the Same Model
Darktrace Autonomous Response alerts
- Antigena / Network / Insider Threat / Antigena Network Scan Block
- Antigena / Network / Insider Threat / Antigena Breaches Over Time Block
- Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Significant Anomaly Block
- Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Breaches over Time Block
- Antigena / Network / Insider Threat / Antigena Large Data Volume Outbound Block
- Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Enhanced Monitoring from Client Block
- Antigena / Network / Insider Threat / Antigena SMB Enumeration Block
- Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Controlled and Model Breach
- Antigena / Network / Insider Threat / Antigena Internal Anomalous File Activity
- Antigena / Network / Significant Anomaly / Antigena Significant Anomaly from Client Block
- Antigena / Network / External Threat / Antigena Ransomware Block
- Antigena / Network / External Threat / SMB Ratio Antigena Block
MITRE ATT&CK techniques observed
Reconnaissance
T1595 — Active Scanning
Resource Development
T1608 — Stage Capabilities
Initial Access
T1190 — Exploit Public-Facing Application
Persistence
T1133 — External Remote Services
Defense Evasion
T1079 — Valid Accounts
Discovery
T1046 — Network Service Scanning
T1083 — File and Directory Discovery
T1018 — Remote System Discovery
Lateral Movement
T1210 — Exploitation of Remote Services
T1080 — Taint Shared Content
T1570 — Lateral Tool Transfer
T1021 — Remote Services
Command and Control
T1071 — Application Layer Protocol
T1095 — Non-Application Layer Protocol
T1571 — Non-Standard Port
Exfiltration
T1041 — Exfiltration over C2 Channel
T1567 — Exfiltration Over Web Service
T1029 — Scheduled Transfer
Impact
T1486 — Data Encrypted for Impact
T1489 — Service Stop
T1529 — System Shutdown/Reboot
































![Cyber AI Analyst Incident Log showing the offending device making over 1,000 connections to the suspicious hostname “zohoservice[.]net” over port 8383, within a specific period.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/662971c1cf09890fd46729a1_Screenshot%202024-04-24%20at%201.55.10%20PM.png)