What is Outlaw Cryptocurrency Mining Operation?
The cybersecurity community has been aware of the threat of Outlaw cryptocurrency mining operation, and its affiliated activities since as early as 2018. Despite its prominence, Outlaw remains largely elusive to researchers and analysts due to its ability to adapt its tactics, procedures, and payloads.
Outlaw gained notoriety in 2018 as security researchers began observing the creation of affiliated botnets.[1][2] Researchers gave Outlaw its name based on the English translation of the “Haiduc” tool observed during their initial activity on compromised devices.[3],[4] By 2019, much of the initial Outlaw activity focused on the targeting of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and other internet facing servers, reportedly focusing operations in China and on Chinese devices.[5],[6] From the outset, mining operations featured as a core element of botnets created by the group.[7] This initial focus may have been a sign of caution by threat actors or a preliminary means of testing procedures and operation efficacy. Regardless, Outlaw actors inevitably expanded scope, targeting larger organizations and a wider range of internet facing devices across geographic scope.
Following a short period of inactivity, security researchers began to observe new Outlaw activity, showcasing additional capabilities such as the ability to kill existing crypto-mining processes on devices, thereby reclaiming devices already compromised by crypto-jacking. [8],[9]
Latest News on Outlaw
Although the more recently observed incidents of Outlaw did demonstrate some new tactics, many of its procedures remained the same, including its unique bundling of payloads that combine crypto-mining and botnet capabilities. [10] In conjunction, the continued use of mining-specific payloads and growth of affiliated botnets has bolstered the belief that Outlaw actors historically prioritizes financial gain, in lieu of overt political objectives.
Given the tendency for malicious actors to share tools and capabilities, true attribution of threat or threat group is extremely difficult in the wild. As such, a genuine survey of activity from the group across a customer base has not always been possible. Therefore, we will present an updated look into more recent activity associated with Outlaw detected across the Darktrace customer base.
Darktrace vs Outlaw
Since late 2022, Darktrace has observed a rise in probable cyber incidents involving indicators of compromise (IoCs) associated with Outlaw. Given its continued prevalence and relative dearth of information, it is essential to take a renewed look at the latest campaign activity associated with threats like Outlaw to avoid making erroneous assumptions and to ensure the threat posed is correctly characterized.
While being aware of previous IoCs and tactics known to be employed in previous campaigns will go some way to protecting against future Outlaw attacks, it is paramount for organizations to arm themselves with an autonomous intelligent decision maker that can identify malicious activity, based on recognizing deviations from expected patterns of behavior, and take preventative action to effectively defend against such a versatile threat.
Darktrace’s anomaly-based approach to threat detection means it is uniquely positioned to detect novel campaign activity by recognizing subtle deviations in affected devices’ behavior that would have gone unnoticed by traditional security tools relying on rules, signatures and known IoCs.
Outlaw Attack Overview & Darktrace Coverage
From late 2022 through early 2023, Darktrace identified multiple cyber events involving IP addresses, domains, and payloads associated with Outlaw on customer networks. In this recent re-emergence of campaign activity, Darktrace identified numerous attack vectors and IoCs that had previously been associated with Outlaw, however it also observed significant deviations from previous campaigns.
Returning Features
As outlined in a previous blog, past iterations of Outlaw compromises include four identified, distinct phases:
1. Targeting of internet facing devices via SSH brute-forcing
2. Initiation of crypto-mining operations
3. Download of shell script and/or botnet malware payloads
4. Outgoing external SSH scanning to propagate the botnet
Nearly all affected devices analyzed by Darktrace were tagged as internet facing, as identified in previous campaigns, supporting the notion that Outlaw continues to focus on easily exposed devices. In addition to this, Darktrace observed three other core returning features from previous Outlaw campaigns in affected devices between late 2022 and early 2023:
1. Gzip and/or Script Download
2. Beaconing Activity (Command and Control)
3. Crypto-mining
Gzip and/or Script Download
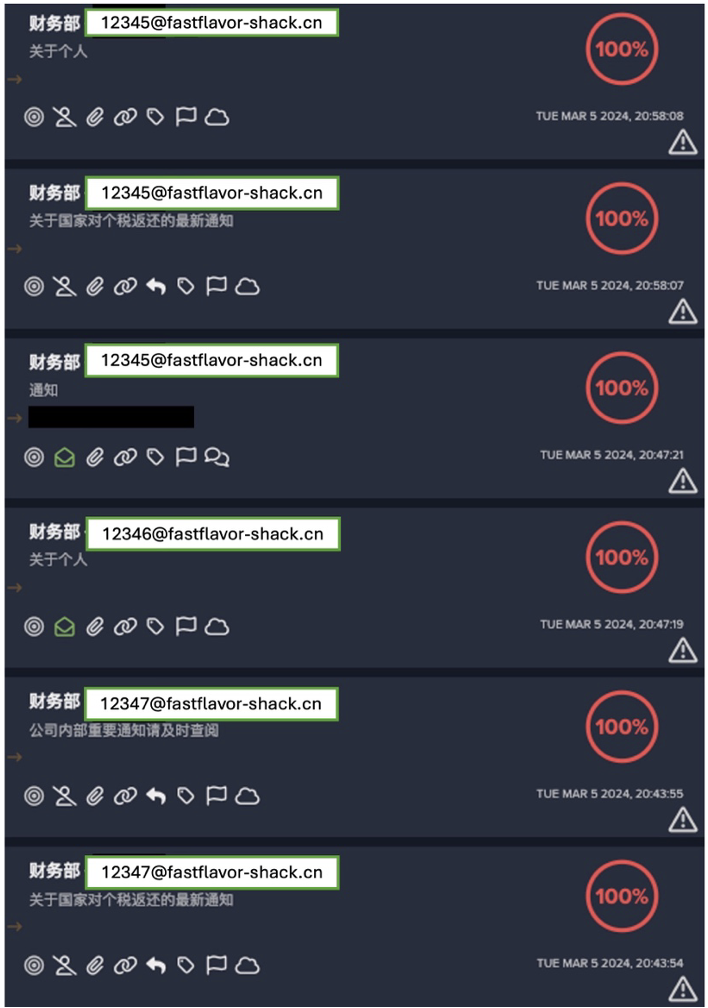
Darktrace observed numerous devices downloading the Dota malware, a strain that is previously known to have been associated with the Outlaw botnet, as either a gzip file or a shell script from rare external hosts.
In some examples, IP addresses that provided the payload were flagged by open-source intelligence (OSINT) sources as having engaged in widespread SSH brute-forcing activities. While the timing of the payload transfer to the device was not consistent, download of gzip files featured prominently during directly observed or potentially affiliated activity. Moreover, Darktrace detected multiple devices performing HTTP requests for shell scripts (.sh) according to detected connection URIs. Darktrace DETECT was able to identify these anomalous connections due to the rarity of the endpoint, payloads, and connectivity for the devices.

Beaconing Activity – Command and Control (C2) Endpoint
Across all Outlaw activity identified by Darktrace, devices engaged in some form of beaconing behavior, rather than one-off connections to IPs associated with Outlaw. While the use of application protocol was not uniform, repeated connectivity to rare external IP addresses related to Outlaw occurred across many analyzed incidents. Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI understood that this beaconing activity represented devices deviating from their expected patterns of life and was able to bring it to the immediate attention of customer security teams.

Crypto-mining
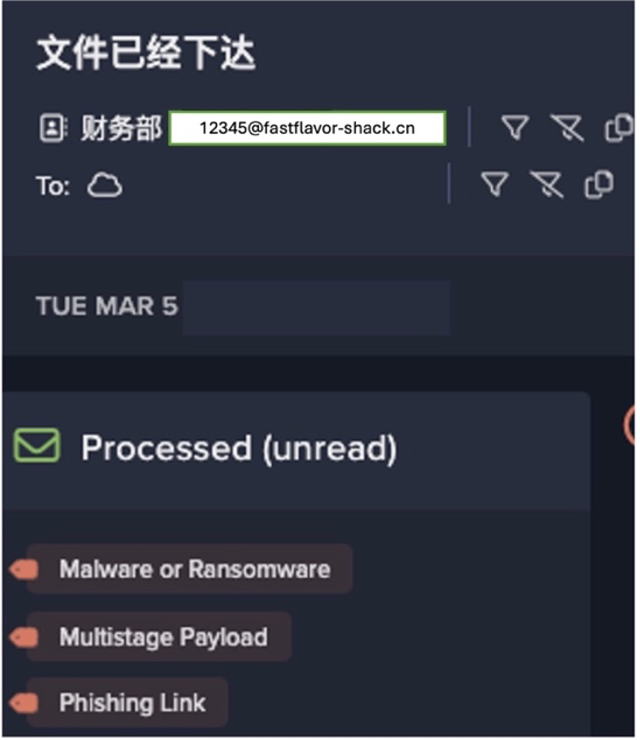
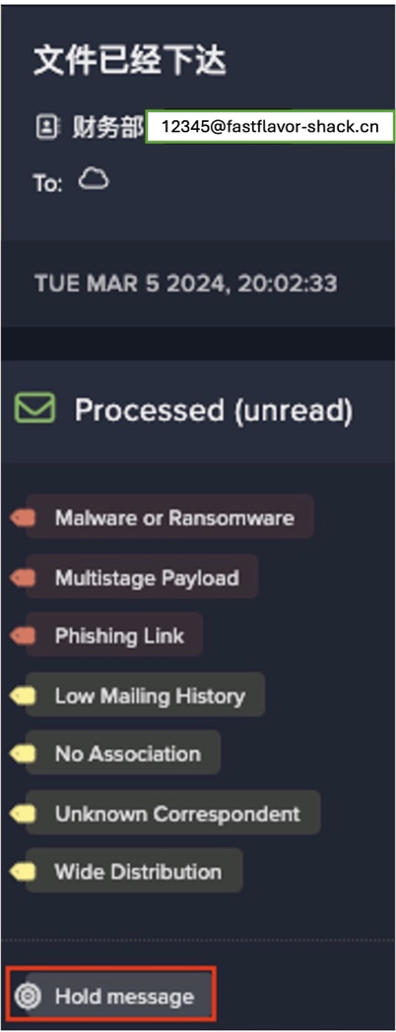
In almost every incident of Outlaw identified across the fleet, Darktrace detected some form of cryptocurrency mining activity. Devices affected by Outlaw were consistently observed making anomalous connections to external endpoints associated with crypto-mining operations. Furthermore, the Minergate protocol appeared consistently across hosts; even when devices did not make direct crypto-mining commands, such hosts attempted connections to external entities that were known to support crypto-mining operations.

Is Outlaw Using New Tactics?
While in the past, Outlaw activity was identified through a systematic kill chain, recent investigations conducted by Darktrace show significant deviations from this.
For instance, affected devices do not necessarily follow the previously outlined kill chain directly as they did previously. Instead, Darktrace observed affected devices exhibiting these phases in differing orders, repeating steps, or missing out attack phases entirely.
It is essential to study such variation in the kill chain to learn more about the threat of Outlaw and how threat actors are continuing to use it is varying ways. These discrepancies in kill chain elements are likely impacted by visibility into the networks and devices of Darktrace customers, with some relevant activity falling outside of Darktrace’s purview. This is particularly true for internet-exposed devices and hosts that repeatedly performed the same anomalous activity (such as making Minergate requests). Moreover, some devices involved in Outlaw activity may have already been compromised prior to Darktrace’s visibility into the network. As such, these conclusions must be evaluated with a degree of uncertainty.
SSH Activity
Although external SSH connectivity was apparent in some of the incidents detected by Darktrace, it was not directly related to brute-forcing activity. Affected devices did receive anomalous incoming SSH connections, however, wide ranging SSH failed connectivity following the initiation of mining operations by compromised devices was not readily apparent across analyzed compromises. Connections over port 22 were more frequently associated with beaconing and/or C2 activity to endpoints associated with Outlaw, than with potential brute-forcing. As such, Darktrace could not, with high confidence correlate such SSH activity to brute-forcing. This could suggest that threat actors are now portioning or rotation of botnet devices for different operations, for example dividing between botnet expansion and mining operations.
Command line tools
In cases of Outlaw investigated by Darktrace, there was also a degree of variability involving the tools used to retrieve payloads. On the networks of customers affected by Outlaw, Darktrace DETECT identified the use of user agents and command line tools that it considered to be out of character for the network and its devices.
When retrieving the Dota malware payload or shell script data, compromised devices frequently relied on numerous versions of wget and curl user agents. Although the use of such tools as a tactic cannot be definitively linked to the crypto-mining campaign, the employment of varying and/or outdated native command line tools attests to the procedural flexibility of Outlaw campaigns, and its potential for continued evolution.

Outlaw in 2023
Given Outlaw’s widespread notoriety and its continued activities, it is likely to remain a prominent threat to organizations and security teams across the threat landscape in 2023 and beyond.
As Darktrace has observed within its customer base from late 2022 through early 2023, activity linked with the Outlaw cryptocurrency mining campaign continues to transpire, offering security teams and research a renewed look at how it has evolved and adapted over the years. While many of its features and tactics appear to have remained consistent, Darktrace has identified numerous signs of Outlaw deviating from its previously known activities.
While relying on previously established IoCs and known tactics from previous campaigns will go some way to protecting an organization’s network from Outlaw compromises, there is a greater need than ever to go further than this. Rather than depending on a list of known-bads or traditional signatures and rules, Darktrace’s anomaly-based approach to threat detection and unparallel autonomous response capabilities mean it is uniquely positioned to DETECT and RESPOND to Outlaw activity, regardless of how it evolves in the future.
Credit to: Adam Potter, Cyber Analyst, Nahisha Nobregas, SOC Analyst, and Ryan Traill, Threat Content Lead
Relevant DETECT Model Breaches:
Compliance / Incoming SSH
Device / New User Agent and New IP
Device / New User Agent
Anomalous Connection / New User Agent to IP Without Hostname
Compromise / Crypto Currency Mining Activity
Anomalous File / Internet Facing System File Download
Anomalous Server Activity / New User Agent from Internet Facing System
Anomalous File / Zip or Gzip from Rare External Location
Anomalous File / Script from Rare External Location
Anomalous Connection / Multiple Failed Connections to Rare Endpoint
Compromise / Large Number of Suspicious Failed Connections
Anomalous Server Activity / Outgoing from Server
Compromise / Sustained TCP Beaconing Activity To Rare Endpoint
Indicators of Compromise
Indicator - Type - Description
/dota3.tar.gz
File URI
Outlaw payload
/tddwrt7s.sh
File URI
Outlaw payload
73e5dbafa25946ed636e68d1733281e63332441d
SHA1 Hash
Outlaw payload
debian-package[.]center
Hostname
Outlaw C2 endpoint
161.35.236[.]24
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
138.68.115[.]96
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
67.205.134[.]224
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
138.197.212[.]204
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
45.9.148[.]59
IP address
Possible Outlaw C2 endpoint
45.9.148[.]117
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
45.9.148[.]125
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
45.9.148[.]129
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
45.9.148[.]99
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
45.9.148[.]234
IP address
Possible Outlaw C2 endpoint
45.9.148[.]236
IP address
Possible Outlaw C2 endpoint
159.203.102[.]122
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
159.203.85[.]196
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
159.223.235[.]198
IP address
Outlaw C2 endpoint
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Tactic -Technique
Initial Access -T1190 Exploit - Public Facing Application
Command and Control - T1071 - Application - Layer Protocol
T1071.001 - Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols
Impact - T1496 Resource Hijacking