Introduction
As malicious actors across the threat landscape continue to look for new ways to gain unauthorized access to target networks, it is unsurprising to see Remote Access Trojans (RATs) leveraged more and more. These RATs are downloaded discretely without the target’s knowledge, typically through seemingly legitimate software downloads, and are designed to gain highly privileged network credentials, ultimately allowing attackers to have remote control over compromised devices. [1]
SectopRAT is one pertinent example of a RAT known to adopt a number of stealth functions in order to gather and exfiltrate sensitive data from its targets including passwords, cookies, autofill and history data stores in browsers, as well as cryptocurrency wallet details and system hardware information. [2]
In early 2023, Darktrace identified a resurgence of the SectopRAT across customer environments, primarily targeting educational industries located in the United States (US), Europe, the Middle East and Africa (EMEA) and Asia-Pacific (APAC) regions. Darktrace DETECT™ was able to successfully identify suspicious activity related to SectopRAT at the network level, as well as any indicators of post-compromise on customer environments that did not have Darktrace RESPOND™ in place to take autonomous preventative action.
What is SectopRAT?
First discovered in early 2019, the SectopRAT is a .NET RAT that contains information stealing capabilities. It is also known under the alias ‘ArechClient2’, and is commonly distributed through drive-by downloads of illegitimate software and utilizes malvertising, including via Google Ads, to increase the chances of it being downloaded.
The malware’s code was updated at the beginning of 2021, which led to refined and newly implemented features, including command and control (C2) communication encryption with Advanced Encryption Stanard 256 (AES256) and additional commands. SectopRAT also has a function called "BrowserLogging", ultimately sending any actions it conducts on web browsers to its C2 infrastructure. When the RAT is executed, it then connects to a Pastebin associated hostname to retrieve C2 information; the requested file reaches out to get the public IP address of the infected device. To receive commands, it connects to its C2 server primarily on port 15647, although other ports have been highlighted by open source intelligence (OSINT), which include 15678, 15649, 228 and 80. Ultimately, sensitive data data gathered from target networks is then exfiltrated to the attacker’s C2 infrastructure, typically in a JSON file [3].
Darktrace Coverage
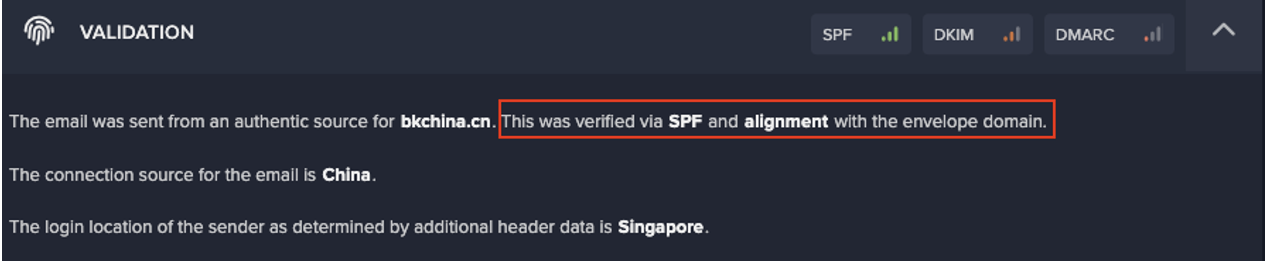
During autonomous investigations into affected customer networks, Darktrace DETECT was able to identify SSL connections to the endpoint pastebin[.]com over port 443, followed by failed connections to one of the IPs and ports (i.e., 15647, 15648, 15649) associated with SectopRAT. This resulted in the devices breaching the ‘Compliance/Pastebin and Anomalous Connection/Multiple Failed Connections to Rare Endpoint’ models, respectively.
In some instances, Darktrace observed a higher number of attempted connections that resulted in the additional breach of the model ‘Compromise / Large Number of Suspicious Failed Connections’.
Over a period of three months, Darktrace investigated multiple instances of SectopRAT infections across multiple clients, highlighting indicators of compromise (IoCs) through related endpoints.Looking specififically at one customer’s activity which centred on January 25, 2023, one device was observed initially making suspicious connections to a Pastebin endpoint, 104.20.67[.]143, likely in an attempt to receive C2 information.
Darktrace DETECT recognized this activity as suspicious, causing the 'Compliance / Pastebin' DETECT models to breach. In response to this detection, Darktrace RESPOND took swift action against the Pastebin connections by blocking them and preventing the device from carrying out further connections with Pastebin endpoints. Darktrace RESPOND actions related to blocking Pastebin connections were commonly observed on this device throughout the course of the attack and likely represented threat actors attempting to exfiltrate sensitive data outside the network.

Around the same time, Darktrace observed the device making a large number of failed connections to an unusual exernal location in the Netherlands, 5.75.147[.]135, via port 15647. Darktrace recognized that this endpoint had never previously been observed on the customer’s network and that the frequency of the failed connections could be indicative of beaconing activity. Subsequent investigation into the endpoint using OSINT indicated it had links to malware, though Darktrace’s successful detection did not need to rely on this intelligence.

After these initial set of breaches on January 25, the same device was observed engaging in further external connectivity roughly a month later on February 27, including additional failed connections to the IP 167.235.134[.]14 over port 15647. Once more, multiple OSINT sources revealed that this endpoint was indeed a malicious C2 endpoint.

While the initial Darktrace coverage up to this point has highlighted the attempted C2 communication and how DETECT was able to alert on the suspicious activity, Pastebin activity was commonly observed throughout the course of this attack. As a result, when enabled in autonomous response mode, Darktrace RESPOND was able to take swift mitigative action by blocking all connections to Pastebin associated hostnames and IP addresses. These interventions by RESPOND ultimately prevented malicious actors from stealing sensitive data from Darktrace customers.

In another similar case investigated by the Darktrace, multiple devices were observed engaging in external connectivity to another malicious endpoint, 88.218.170[.]169 (AS207651 Hosting technology LTD) on port 15647. On April 17, 2023, at 22:35:24 UTC, the breach device started making connections; of the 34 attempts, one connection was successful – this connection lasted 8 minutes and 49 seconds. Darktrace DETECT’s Self-Learning AI understood that these connections represented a deviation from the device’s usual pattern of behavior and alerted on the activity with the ‘Multiple Connections to new External TCP Port’ model.


A few days later, on April 20, 2023, at 12:33:59 (UTC) the source device connected to a Pastebin endpoint, 172.67.34[.]170 on port 443 using the SSL protocol, that had never previously be seen on the network. According to Advanced Search data, the first SSL connection lasted over two hours. In total, the device made 9 connections to pastebin[.]com and downloaded 85 KB of data from it.

Within the same minute, Darktrace detected the device beginning to make a large number of failed connections to another suspicious endpoints, 34.107.84[.]7 (AS396982 GOOGLE-CLOUD-PLATFORM) via port 15647. In total the affected device was observed initiating 1,021 connections to this malicious endpoint, all occurring over the same port and resulting the failed attempts.

Conclusion
Ultimately, thanks to its Self-Learning AI and anomaly-based approach to threat detection, Darktrace was able to preemptively identify any suspicious activity relating to SectopRAT at the network level, as well as post-compromise activity, and bring it to the immediate attention of customer security teams.
In addition to the successful and timely detection of SectopRAT activity, when enabled in autonomous response mode Darktrace RESPOND was able to shut down suspicious connections to endpoints used by threat actors as malicious infrastructure, thus preventing successful C2 communication and potential data exfiltration.
In the face of a Remote Access Trojan, like SectopRAT, designed to steal sensitive corporate and personal information, the Darktrace suite of products is uniquely placed to offer organizations full visibility over any emerging activity on their networks and respond to it without latency, safeguarding their digital estate whilst causing minimal disruption to business operations.
Credit to Justin Torres, Cyber Analyst, Brianna Leddy, Director of Analysis
Appendices
Darktrace Model Detection:
- Compliance / Pastebin
- Anomalous Connection / Multiple Failed Connections to Rare Endpoint
- Compromise / Large Number of Suspicious Failed Connections
- Anomalous Connection / Multiple Connections to New External TCP Port
List of IoCs
IoC - Type - Description + Confidence
5.75.147[.]135 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
5.75.149[.]1 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
34.27.150[.]38 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
34.89.247[.]212 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
34.107.84[.]7 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
34.141.16[.]89 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
34.159.180[.]55 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
35.198.132[.]51 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
35.226.102[.]12 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
35.234.79[.]173 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
35.234.159[.]213 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
35.242.150[.]95 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
88.218.170[.]169 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
162.55.188[.]246 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
167.235.134[.]14 - IP - SectopRAT C2 Endpoint
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
Model: Compliance / Pastebin
ID: T1537
Tactic: EXFILTRATION
Technique Name: Transfer Data to Cloud Account
Model: Anomalous Connection / Multiple Failed Connections to Rare Endpoint
ID: T1090.002
Sub technique of: T1090
Tactic: COMMAND AND CONTROL
Technique Name: External Proxy
ID: T1095
Tactic: COMMAND AND CONTROL
Technique Name: Non-Application Layer Protocol
ID: T1571
Tactic: COMMAND AND CONTROL
Technique Name: Non-Standard Port
Model: Compromise / Large Number of Suspicious Failed Connections
ID: T1571
Tactic: COMMAND AND CONTROL
Technique Name: Non-Standard Port
ID: T1583.006
Sub technique of: T1583
Tactic: RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
Technique Name: Web Services
Model: Anomalous Connection / Multiple Connections to New External TCP Port
ID: T1095
Tactic: COMMAND AND CONTROL
Technique Name: Non-Application Layer Protocol
ID: T1571
Tactic: COMMAND AND CONTROL
Technique Name: Non-Standard Port
References
1. https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/RAT-remote-access-Trojan
2. https://malpedia.caad.fkie.fraunhofer.de/details/win.sectop_rat